Repressive drug policy in CEECA region causes constant and severe human rights violations of people who use drugs. Every year thousands of people who use drugs go to jail for victimless crimes, they are denied treatment, discriminated by social services, abused by police, have limited job and educational opportunities. Most of those rights are guranteed by national constitutions and international human rights treaties and states are obliged to ensure and protect them. Currently, there are nine human rights international treaties, and one optional protocol, from which 10 treaty bodies have been established. Most CEECA countries have signed and/or ratified international human rights treaties and most CEECA countries’ constitutions recognize supremacy of these treaties over the country’s national laws. The following treaties might be applied to drug policy issues:
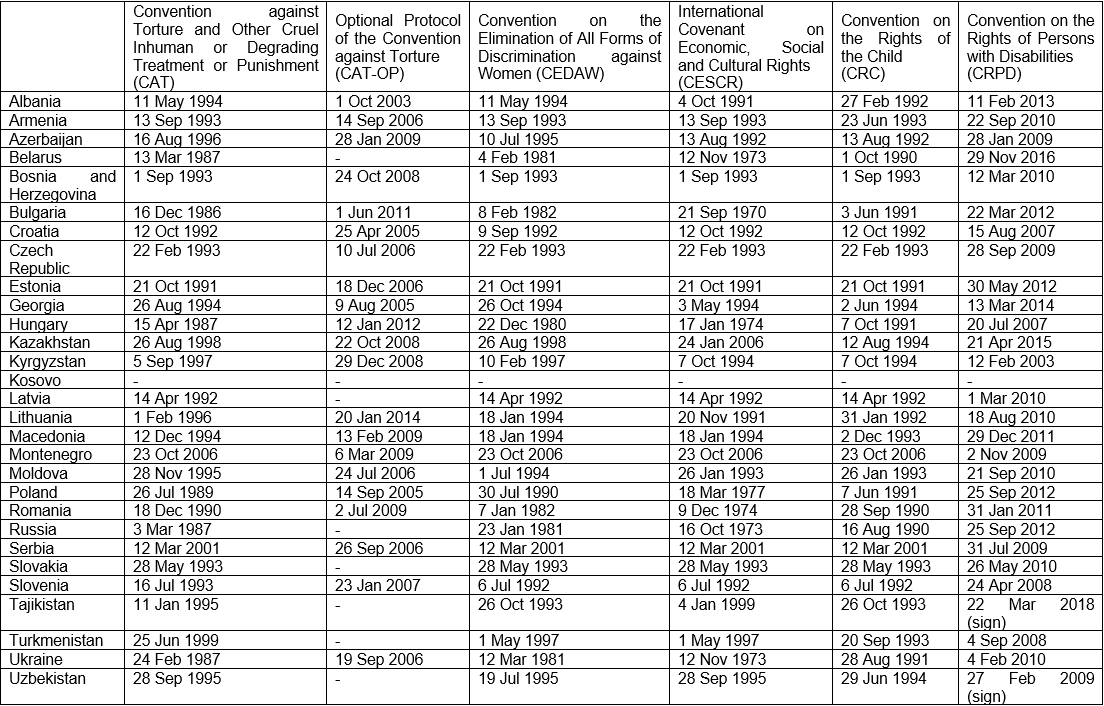
- Convention against Torture and Other Cruel Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment
- Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women
- International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights
- Convention on the Rights of the Child
- Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities
Each of the treaties has at least one of the following monitoring mechanisms:
- Country report review procedure means that special human rights body reviews how countries fulfill treaty obligations. On average every country undergoes a review of at least one human rights body every 4 to 5 years. You can find out your country’s due date here https://tbinternet.ohchr.org/_layouts/TreatyBodyExternal/MasterCalendar.aspx
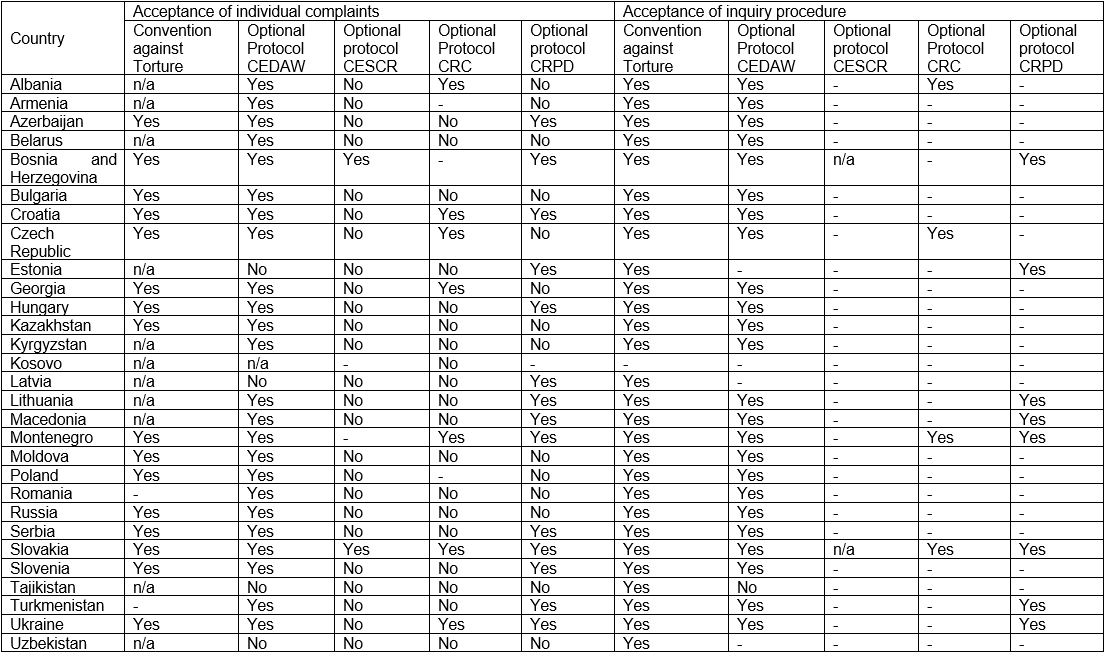
- Individual complaint procedure means that s a treaty monitoring body accepts individual complaints. An individual does not need to be a national of that state in order to be able to file an application against it. The most important factor is that the human rights violation happened on the territory of a particular state or a particular state is responsible for a human rights violation that happened outside of its territory.
- Inquiry procedure allows treaty monitoring body to conduct an independent investigation based on requests from individuals or groups claiming systematic and serious violations of human rights guaranteed by a one of the treaties.
Cycle of reporting to the Committie within country review procedure:
- The state prepares the report and sends it to the Committee
- Civil society submits alternative reports
- The Committee invites civil society for consultation
- The Committee publishes its questions to the government
- The state answers the questions in writing
- Civil society submits its comments to the state’s reply
- Committie meets with state representatives to discuss the report and raised questions, civil society is allowed to interfere and ask additional questions
- Committee prepares and sends its recommendations for the state
- Civil society can observy the state’s comlience to the Committee’s recomendations
Ratification Status of the conventions
Individual complaints and inquiry procedure
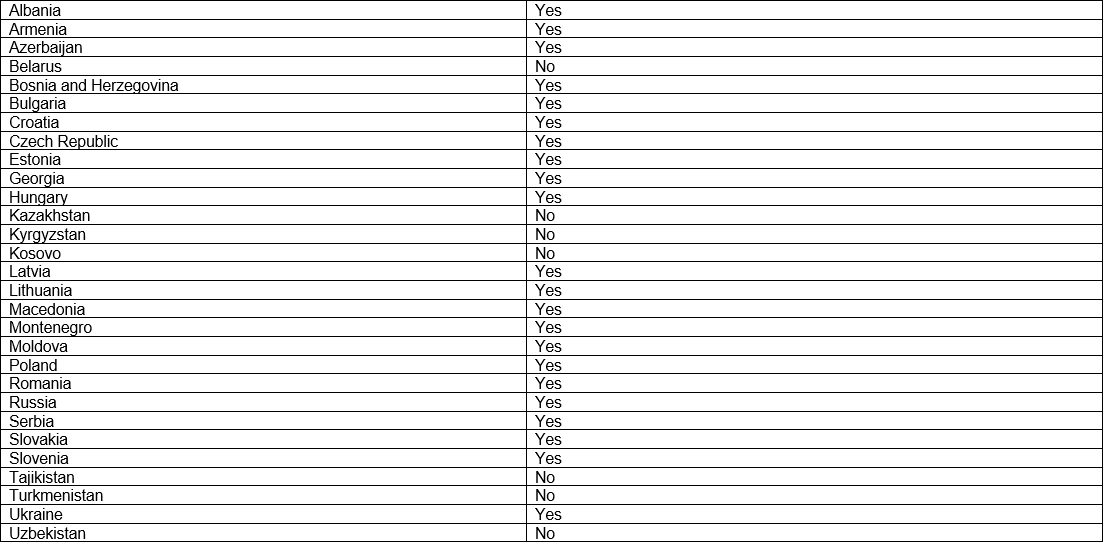
Council of Europe includes 47 countries and is one of the leading organizations in the field of human rights. The fundamental document of the Council of Europe is the European Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms (the European Convention on Human Rights). There are several human rights mechanisms within the Council of Europe:
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) is a treaty monitoring body for Convention on Human Rights wich can review individual complaints and issue judgments which are binding for member states
The Commissioner for Human Rights is an independent official whose task is to promote human rights education, attention to human rights and their observance in the CoE countries. The Commissioner does not accept individual complaints but conducts visits to countries.
Committee of Ministers the main functions of which are the promotion of political dialogue between the governments of the member countries, the admission of states to the Organization, control over the fulfillment of their obligations, development and adoption of conventions and agreements, approval of the program of activities and budget of the Council of Europe, as well as monitoring their implementation. An important function of the CMCE is to monitor the implementation of decisions of the European Court of Human Rights.
The Committee for the Prevention of Torture, Inhumane and Degrading Treatment and Punishment visits places of detention, police stations and psychiatric hospitals
The European Committee for Social Rights monitors compliance by states with the obligations they have undertaken under the European Social Charter
The Parliamentary Assembly is one of the two main statutory bodies of the Council of Europe and represents the interests of the main political parties that exist in the member states of the Organization. There are 3 Commissions within the Parliamentary Assembly, which deals with human rights: Commission on Legal Affairs and Human Rights, Commission for Equal Opportunities for Women and Men, Monitoring Commission (this commission also monitors the way member states fulfill their commitments made after they joined the Council of Europe).
CEECA countries that are part of the Council of Europe
Other international human rights organizations:
- Amnesty International
- Human Rights Watch
- IWRAW Asia Pacific works with women and helps with submitting applications to CEDAW
Texts of all of the conventions https://treaties.un.org/Pages/Treaties.aspx?id=4&subid=A&lang=en